Operations
Admin Wizard
The Quick Start wizard allows you to perform the following Hue setup operations by clicking the tab of each step or sequentially by clicking Next in each screen:
- Check Configuration validates your Hue configuration. It will note any potential misconfiguration and provide hints as to how to fix them. You can edit the configuration file described in the next section.
- Connectors The list of services to query or browse
- Examples get started with examples of SQL tables, queries, workflows and jobs to run.
- Users contains a link to the User Admin application to create or import users and a checkbox to enable and disable collection of usage information.
Configuration
Displays a list of the installed Hue applications and their configuration.
Hue ships with a default configuration that assumes a various set of services to be present in the cluster. If you are running on a real cluster, you can customize the hue.ini configuration file (/etc/hue/hue.ini when installed from the package version) or pseudo-distributed.ini in desktop/conf when in development mode).
Click the tabs under Configuration Sections to see the settings configured for each application. For information on configuring these settings, see Configuration.
Hue loads and merges all of the files with extension .ini located in the /etc/hue directory. Files that are alphabetically later take precedence.
After editing the ini file, Hue needs to be restarted.
Configuration Validation
To view the configuration of a running Hue instance, navigate to:
http://<hue>/hue/dump_config
The location of the folder containing the Hue ini files is shown at the top of the page as well as all the configuration values with help and information on the default values.
To list all available configuration options via the command line, run:
/usr/share/hue/build/env/bin/hue config_help | less
Server Logs
Displays the Hue Server log and allows you to download them to your local system in a zip file.
Threads
Threads page can be very helpful in debugging purposes. It includes a daemonic thread and the thread objects serving concurrent requests. The host name, thread name identifier and current stack frame of each are displayed. Those are useful when Hue “hangs”, sometimes in case of a request too CPU intensive. There is also a REST API to get the dump of Threads using desktop/debug/threads.
Metrics
Hue uses the PyFormance Python library to collect the metrics. These metrics are represented as gauge, counters, meter, rate of events over time, histogram, statistical distribution of values. A REST API endpoint /desktop/metrics/ to get all the metrics dump as json is also exposed
The below metrics of most concern to us are displayed on the page:
- requests.active
- requests.exceptions
- requests.response-time
- threads.daemon
- threads.total
- users
- users.active
One of the most useful ones are the percentiles of response time of requests and the count of active users. Admins can either filter a particular property in all the metrics or select a particular metric for all properties
Logging
The Hue logs are found in /var/log/hue, or in a logs directory under your
Hue installation root. Inside the log directory you can find:
- An
access.logfile, which contains a log for all requests against the Hue web server. - A
supervisor.logfile, which contains log information for the supervisor process. - A
supervisor.outfile, which contains the stdout and stderr for the supervisor process. - A
.logfile for each supervised process described above, which contains the logs for that process. - A
.outfile for each supervised process described above, which contains the stdout and stderr for that process.
If users on your cluster have problems running Hue, you can often find error messages in these log files. If you are unable to start Hue from the init script, the supervisor.log log file can often contain clues.
In addition to logging INFO level messages to the logs directory, the Hue web server keeps a small buffer of log messages at all levels in memory. You can view these logs by visiting http://myserver:8888/hue/logs. The DEBUG level messages shown can sometimes be helpful in troubleshooting issues.
Commands
Commands are utils handy for performing some tasks like update some user password, creating a super user, cleaning-up old sessions and documents.
Type the following command from the Hue installation root.
cd /usr/lib/hue (or /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH-XXXXX/share/hue if using parcels and CM)
To list all the available commands:
build/env/bin/hue
> Type 'hue help <subcommand>' for help on a specific subcommand.
Available subcommands:
[auth]
changepassword
createsuperuser
[axes]
axes_list_attempts
axes_reset
[beeswax]
beeswax_install_examples
beeswax_install_examples_tests
close_queries
close_sessions
create_table_query_data
[contenttypes]
remove_stale_contenttypes
[desktop]
config_dump
config_help
config_override
config_upgrade
convert_documents
create_desktop_app
create_proxy_app
create_test_fs
create_user_directories
desktop_document_cleanup
generate_mdl
is_db_alive
kt_renewer
ldaptest
runcelery
runcherrypyserver
runcpserver
rungunicornserver
runpylint
sync_documents
syncdb
test
version
[django]
check
compilemessages
createcachetable
dbshell
diffsettings
dumpdata
flush
inspectdb
loaddata
makemessages
makemigrations
migrate
sendtestemail
shell
showmigrations
sqlflush
sqlmigrate
sqlsequencereset
squashmigrations
startapp
startproject
testserver
[django_extensions]
admin_generator
clean_pyc
clear_cache
compile_pyc
create_app
create_command
create_jobs
create_template_tags
delete_squashed_migrations
describe_form
drop_test_database
dumpscript
export_emails
find_template
generate_secret_key
graph_models
mail_debug
notes
passwd
pipchecker
print_settings
print_user_for_session
reset_db
runjob
runjobs
runprofileserver
runscript
runserver_plus
set_default_site
set_fake_emails
set_fake_passwords
shell_plus
show_template_tags
show_templatetags
show_urls
sqlcreate
sqldiff
sqldsn
sync_s3
syncdata
unreferenced_files
update_permissions
validate_templates
[indexer]
indexer_setup
[notebook]
dbproxy_server
notebook_setup
send_query_stats
[oozie]
oozie_setup
[sessions]
clearsessions
[staticfiles]
collectstatic
findstatic
runserver
[useradmin]
import_ldap_group
import_ldap_user
sync_ldap_users_and_groups
useradmin_sync_with_unix
Troubleshooting
Instrumentation
To troubleshoot why Hue is slow or consuming high memory, admin can enable instrumentation by setting the instrumentation flag to True.
[desktop]
instrumentation=true
If django_debug_mode is enabled, instrumentation is automatically enabled. This flag appends the response time and the total peak memory used since Hue started for every logged request.
Instrumentation enabled:
[17/Apr/2018 15:18:43 -0700] access INFO 127.0.0.1 admin - "POST /jobbrowser/jobs/ HTTP/1.1" `returned in 97ms (mem: 135mb)`
Instrumentation not enabled:
[23/Apr/2018 10:59:01 -0700] INFO 127.0.0.1 admin - "POST /jobbrowser/jobs/ HTTP/1.1" returned in 88ms
Change or reset a password
Via the Hue commands, to change the password of the currently logged in Unix user:
build/env/bin/hue changepassword
If you don’t remember the admin username, create a new Hue admin (you will then also be able to login and could change the password of another user in Hue):
build/env/bin/hue createsuperuser
Make a certain user admin
It is recommended to just do it as an admin via the Admin UI.
In case this is not possible (e.g. nobody is admin), doing it on the command line is explained in the examples of the Python API.
At the last recourse, the database user records can be updated via SQL.
Exporting Documents
Export all documents:
./build/env/bin/hue dumpdata desktop.Document2 --indent 2 --natural > data.json
Export specific documents:
20000013 is the id you can see in the URL of the dashboard.
./build/env/bin/hue dumpdata desktop.Document2 --indent 2 --pks=20000013 --natural > data.json
You can specify more than one id:
--pks=20000013,20000014,20000015
Load the documents:
./build/env/bin/hue loaddata data.json
Large downloads
Download and export options with limited scalability unless using the Task Server is enabled. Restrict the number of rows or bytes transferred using the following options respectively in your hue.ini.
Slow because too documents
When the database has too many entries, it will cause performance issue. The config check will help superuser to find this issue. Login as superuser and go to “Hue Administration”, this sample screenshot will be displayed in the quick start wizard when the tables have too many entries.
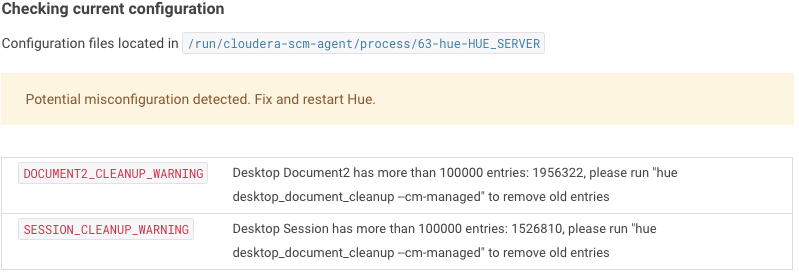
To clean up Hue database, go to Hue directory and run following clean up command:
./build/env/bin/hue desktop_document_cleanup
Too many connections
When getting an error similar to OperationalError: (1040, 'Too many connections'), this indicates that the Hue database is overloaded and out of connections. Hue only needs 2 but often the database is used by other services that might “hog” them. Increasing max_connections to around 1000 should be sufficient. e.g. for MySQL, connect to it and set below parameter:
mysql> SET GLOBAL max_connections = 1000;
Testing SQL connection from a Pod
First check your Hive version in the SQL Editor:
SELECT version()
> 2.3.2 r857a9fd8ad725a53bd95c1b2d6612f9b1155f44d
Then list the Hue pods:
kubectl get pods
> NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hue-758466dc77-wpcx8 2/2 Running 0 22h
ingress-nginx-controller-5d6fbbddb6-8kd86 1/1 Running 0 23h
postgres-hue-64c9cc8744-dpk47 1/1 Running 1 47d
Connect to it:
kubectl exec -it hue-758466dc77-wpcx8 hue -- bash
Then get the client files of the same Hive version from:
https://archive.apache.org/dist/hadoop/core
https://archive.apache.org/dist/hive
And install them:
sudo apt-get install wget
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/hadoop/core/hadoop-2.7.4/hadoop-2.7.4.tar.gz
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/hive/hive-2.3.2/apache-hive-2.3.2-bin.tar.gz
tar -xvzf hadoop-2.7.4.tar.gz
tar -xvzf apache-hive-2.3.2-bin.tar.gz
export HADOOP_HOME=`pwd`/hadoop-2.7.4
export HIVE_HOME=`pwd`/apache-hive-2.3.2-bin
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.11.0-openjdk-amd64
PATH=$PATH:$HIVE_HOME/bin
And now you are ready to connect:
beeline -u 'jdbc:hive2://172.21.0.3:10000'
> SLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings.
SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/share/hue/apache-hive-2.3.2-bin/lib/log4j-slf4j-impl-2.6.2.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/share/hue/hadoop-2.7.4/share/hadoop/common/lib/slf4j-log4j12-1.7.10.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation.
SLF4J: Actual binding is of type [org.apache.logging.slf4j.Log4jLoggerFactory]
Connecting to jdbc:hive2://172.21.0.3:10000
Connected to: Apache Hive (version 2.3.2)
Driver: Hive JDBC (version 2.3.2)
Transaction isolation: TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ
Beeline version 2.3.2 by Apache Hive
0: jdbc:hive2://172.21.0.3:10000> SHOW TABLES;
+--------------------+
| tab_name |
+--------------------+
| about |
| amandine_test |
| city_cases |
| cricketer |
| cust1 |
| cust2 |
| customer |
| customers |
| student_info |
| ........ |
| web_logs |
| yash_contact_test |
+--------------------+
52 rows selected (0.098 seconds)
Read more on the Hive wiki about the beeline command line.
Scripts
For building custom scripts for managing objects like users or saved documents, check out the Python API.
Database
See the dedicated Database section.